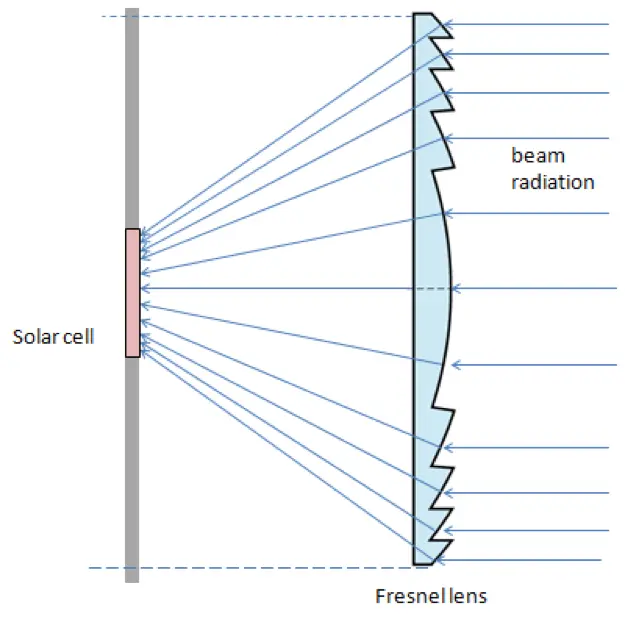
What are concentrating photovoltaics? One of the ways to increase the output from the photovoltaic systems is to supply concentrated light onto the PV cells. This can be done by using optical light collectors, such as lenses or mirrors. The PV systems that use concentrated light are called concentrating photovoltaics (CPV). The CPV collect light from a larger area and concentrate it to a smaller area solar cell. This is illustrated in Figure 5.1.
Also, from the article - 33.6% efficiency in real-world conditions:
A 60 cell-lens prototype was studied for a year. In "real-world" conditions, CPVs achieved up to 33.6% efficiency. The 36% mark was posted at 167 degrees Fahrenheit. The prototype showed no signs of degradation, according to IE.